Fiscalization and E-invoicing in Albania (B2B and B2C in 2025)
Albania mandates real-time e-invoicing for all B2G, B2B, and B2C transactions through the Central Invoice Platform using structured UBL or XML formats.


Last modified on 2025-12-19 in Blog
UN/CEFACT, UBL 2.1
Central Information System (CIS)
General Directorate of Taxation (GDT)
Fizkalizimi
2019
2021
5 years
Albania has already taken a major step in modernising its tax system through mandatory e-invoicing. Under Law No. 87/2019, the government introduced electronic invoicing in phases, starting with B2G transactions on January 1, 2021, expanding to B2B on July 1, 2021, and covering all cash transactions from September 1, 2021.
Companies in Albania must issue e-invoices in structured formats such as UBL 2.1 or the UN/CEFACT XML standard, as required by Law 87/2019 and related guidance from the tax authorities. These formats allow invoices to be processed digitally through the central platform, helping businesses reduce errors, streamline reporting, and simplify compliance with national standards. By adopting these digital formats, companies can improve efficiency, enhance transparency, and manage their financial operations more effectively.

Albania has been steadily implementing its e-invoicing system under Law No. 87/2019. All businesses issuing invoices must now use structured digital formats such as UBL 2.1 or UN/CEFACT XML, and invoices must be transmitted in real time to the Central Information System (CIS) managed by the General Directorate of Taxes.
The government recently reminded companies that every business must hold a valid digital certificate from AKSHI to issue and sign e-invoices. Authorities are emphasizing compliance to ensure proper reporting, reduce tax errors, and improve transparency, with businesses urged to update their systems and processes in line with the technical standards.

You do not need to know anything about e-invoicing standards or real-time reporting.
E-invoicing in Albania means issuing and receiving invoices in structured electronic formats such as UBL 2.1 or UN/CEFACT XML, instead of paper or simple PDFs. This allows businesses to process invoices digitally, reduce manual errors, and simplify reporting to the tax authorities.
Albania has made e-invoicing mandatory under Law No. 87/2019 to improve tax transparency, reduce informal transactions, and enable real-time monitoring of business activity. To support this system, the government operates a Central Information System (CIS) through the General Directorate of Taxes (DPT), while the National Agency for Information Society (AKSHI) manages digital certificates and ensures secure electronic signing of invoices.
The rules were introduced in phases, B2G invoices from January 1, 2021, B2B from July 1, 2021, and all cash transactions from September 1, 2021. Every business issuing invoices must comply with these formats and have a valid digital certificate, helping Albania modernize its invoicing system, fight tax evasion, and align with EU technical standards for e-invoicing.
Albania’s e-invoicing system is designed to keep up with European standards and the EU’s push for digital, transparent VAT reporting. By using structured formats like UBL and sending invoices to the tax system in real time it makes sure everything runs smoothly and in line with modern European practices.
This makes life easier for businesses, especially those trading with EU countries, because invoices can be tracked and verified quickly, reducing errors and preventing tax fraud. With the EU’s VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) initiative moving toward real-time, structured e-invoices across Europe, Albania is setting itself up to stay in step with future EU digital rules as it moves closer to EU membership.
In Albania, e-invoicing for public sector transactions became mandatory on 1 January 2021 under Law No. 87/2019. Any business that issues invoices to government institutions must send them electronically through the Central Invoice Platform, the system managed by the Albanian tax authority. To access the platform, companies need a valid electronic certificate issued by AKSHI, ensuring secure identification and data exchange.
All B2G invoices must be created in electronic form and transmitted in real time to the tax authority. Banks and financial institutions also report related non-cash payments daily, helping increase transparency in government spending and improving the accuracy of public-sector financial records.
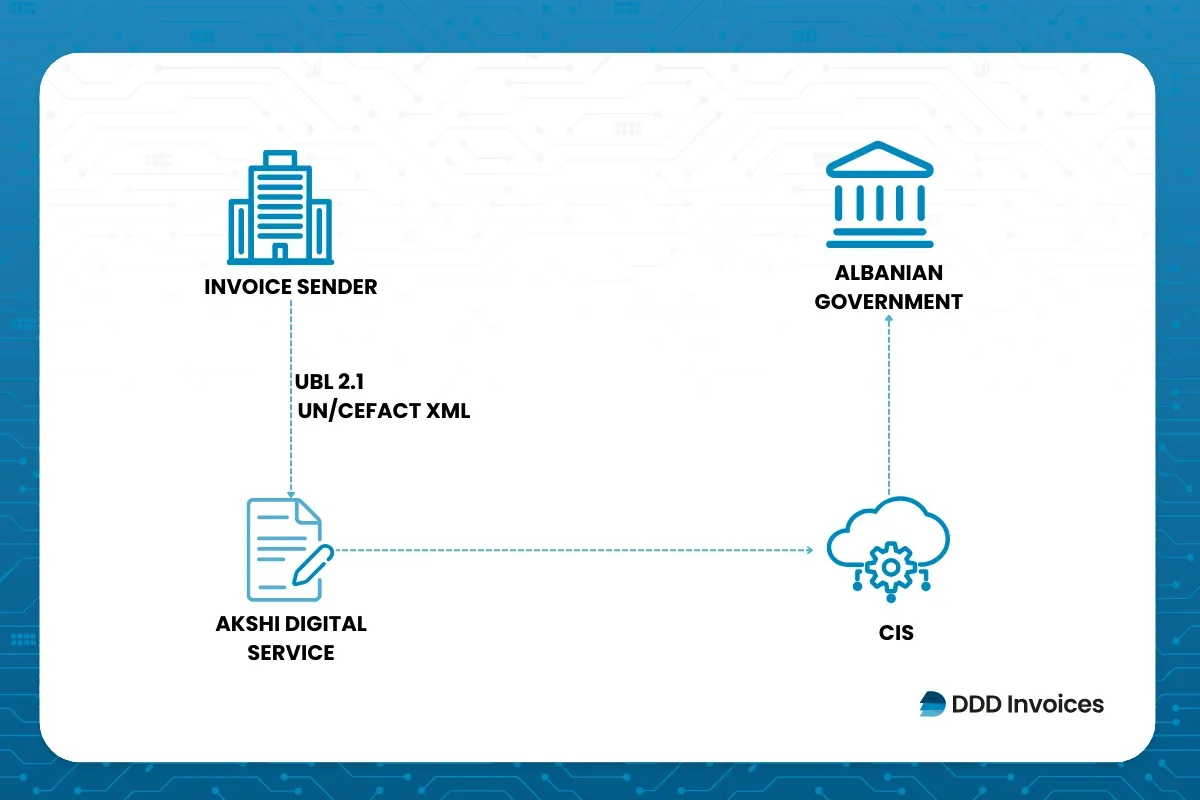
From 1 July 2021, e-invoicing became mandatory for all non-cash B2B transactions in Albania under Law No. 87/2019. Businesses must issue and transmit invoices electronically through the Central Invoice Platform, ensuring that invoice data is reported in real time to the tax authority.
Companies need a digital certificate from AKSHI to issue and sign e-invoices. Banks and other financial institutions processing non-cash payments must report them daily to the tax authority through the e-Invoice Bank Service. This ensures accurate reporting, better monitoring of transactions, and compliance with Albanian tax rules.
In Albania, e-invoicing for B2C transactions became mandatory for all cash sales starting 1 September 2021 under Law No. 87/2019. Businesses must issue electronic invoices through the Central Invoice Platform, ensuring that every sale to consumers is recorded and transmitted to the tax authority in real time.
To comply, companies must use certified invoicing systems connected to the platform. These systems help prevent tax fraud, maintain accurate transaction records, and provide transparency for audits, making consumer billing more secure and traceable.
In Albania, businesses that sell directly to consumers such as shops, restaurants, and service providers, must use certified invoicing or cash register systems. These systems ensure that every sale, whether paid by cash or card, is recorded securely and transmitted in real time to the tax authority. Once a sale is recorded, the data cannot be altered or deleted, helping prevent fraud and maintain accurate reporting. This is part of Albania’s broader effort to improve transparency, trust, and fairness in business transactions.
.webp&w=640&q=75)
In Albania, e-reporting makes it easier for businesses to share accurate VAT and sales information with the tax authorities using the Central Invoice Platform. In addition to real-time invoice reporting, businesses are required to comply with VAT obligations and maintain proper sales and purchase records in line with Albanian tax law. This system, part of Albania’s move to modernize its tax processes under Law No. 87/2019, helps businesses stay compliant, avoid mistakes, and get ready for the wider use of e-invoicing and real-time reporting.
If a business in Albania doesn’t follow the fiscalisation rules in Law 87/2019, such as not issuing invoices through the Central Invoice Platform, not using certified software, or failing to report cash and non-cash payments, it can face penalties from the tax authority.
All registered businesses are required to issue and fiscalize invoices using valid digital certificates from AKSHI. The law gives the tax authority the power to apply fines or other penalties for non-compliance, and in many cases, businesses are given the chance to correct mistakes. These rules are designed to improve transparency, reduce undeclared transactions, and ensure that all sales are properly recorded in real time.
Albania’s move to mandatory e-invoicing can feel overwhelming, but DDD Invoices is here to make it simple. From issuing invoices through the Central Invoice Platform to ensuring you’re fully compliant with all Albanian tax rules, our platform helps you stay on top of every requirement.
With DDD Invoices, you can send invoices correctly on time, report payments in real time, and avoid errors that could lead to penalties. Whether you’re a small business, a growing company, or a software provider, we make e-invoicing easy, fast, and reliable.
Still have questions?
In the 30min free call we will discuss:
All VAT-registered businesses in Albania must issue and receive invoices electronically through the Central Invoice Platform. This includes companies of all sizes, from small businesses to large corporations. Cash and non-cash transactions must be reported in real time, and paper invoices are no longer sufficient for compliance.
If your business fails to send invoices correctly or does not report payments on time, you can face fines of 50,000 Lek per violation. Repeated or serious violations may trigger additional administrative measures. It’s important to ensure your invoicing system is compliant and tested to avoid penalties.
Invoices must be sent through the Central Invoice Platform using a certified system. Businesses also need a valid AKSHI digital certificate to ensure every invoice is secure and recognized by the tax authority. These systems automatically report transaction details in real time and help prevent errors or fraud.
Yes. All sales to consumers, including cash and card payments, must be recorded through certified invoicing systems. While structured e-invoices for B2C are not mandatory in the same way as B2B, all transactions must be reported in real time to the tax authority to ensure transparency and prevent tax evasion.
Written by the Compliance team
Reviewed by Denis V. P.